Remove Action and Adding the Action Again
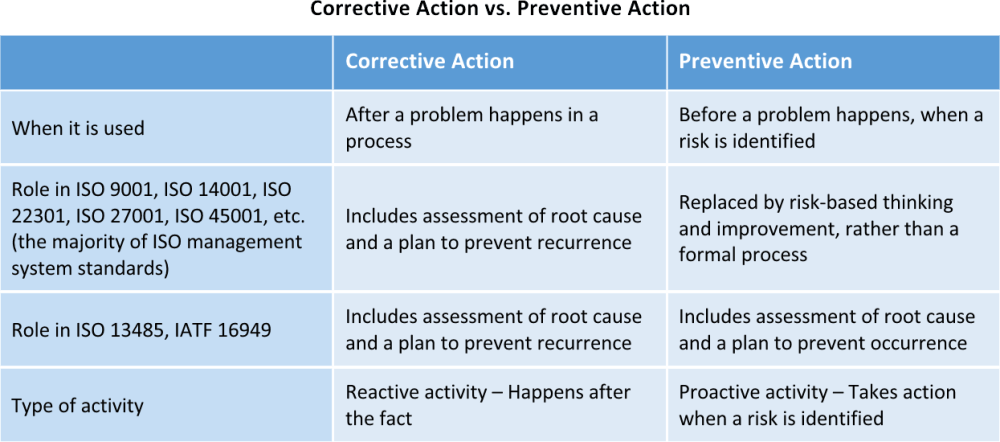
What is a preventive action?
Preventive action is taken to fix the cause of a procedure trouble before it tin happen. In a management arrangement, a preventive action (PA) definition could exist: "the activities taken by the organization to eliminate the cause of a potential process nonconformity." If y'all are identifying potential issues that could happen in a process, assessing what could crusade these bug, and taking action to prevent the problem from occurring earlier information technology happens, so you are taking preventive activity.
What is corrective action?
Corrective activity (CA) is the activities taken to eliminate the cause of a process nonconformity. Corrective action is the activity of reacting to a process problem, getting it under command through containment actions, and then taking the action needed to stop information technology from happening again. Earlier versions of ISO 9001 made the stardom that CA will preclude recurrence of a problem, but PA will prevent the occurrence of the problem.
Cosmetic and preventive action examples
Cosmetic actions take steps to ready the cause of a trouble after the problem has occurred, whereas preventive deportment notice the problem before it occurs and takes steps to fix the cause of the problem before it happens.
Here is a unproblematic corrective action and preventive action (CAPA) instance:
- Cosmetic activity – I injure myself on the corner of a tabular array, find that the cause is that the table has sharp corners, and have activeness to make the tabular array accept rounded corners so that no 1 else gets hurt. This includes the deportment to change the design so that futurity tables made will accept rounded corners.
- Preventive activity – I observe that the corners of a tabular array could cut someone (even though no one has been injured), then find that the crusade is the abrupt corners, and take action to round the corners and change the future design to accept round corners.
This is an example that uses a production trouble, where CAPA in the direction system ordinarily involves process issues, but with this example it is piece of cake to encounter the divergence between preventive actions and corrective actions. In brusque, cosmetic actions are reactive to a problem subsequently information technology happens, where preventive actions are proactive to a potential trouble before it can happen.
Why do the recent ISO standards require cosmetic activity and not preventive action?
The previous versions of ISO 27001, ISO 9001, ISO 14001, and other standards that align with Annex SL included requirements for a corrective action process and a preventive action process as part of the direction system. The steps involved in both were substantially the same, just the activeness that triggered the procedure was unlike; corrective activeness reacted to a problem that occurred, where preventive action was initiated past the identification of a potential problem. In that location was oftentimes defoliation about this when implementing before versions of these management systems; some people only used their preventive activity process a few times, as it is a complex process and takes time away from reacting through corrective deportment. All the same other people interpreted any activity during the corrective action process to prevent a recurrence to be preventive action.
So, now the most recent release of the management system standards aligned with Annex SL, such as ISO 27001:2013, ISO 9001:2015, and ISO 14001:2015, don't require preventive action whatsoever longer. In some ways, this prevents the confusion mentioned above, but in other ways, ISO has indicated that the complex process that was previously involved in PA is unnecessary, and at that place are other parts of the standard that, when used properly, can effectively provide good preventive actions. Now preventive action is replaced by other parts of the standard, including:
- Gamble-based thinking – This new requirement asks that you lot identify areas that could affect the management system where you are uncertain of the outcome. This way of thinking entails identifying this doubt, or risk, and determining if you lot need to take action to foreclose bad outcomes or to capitalize on positive outcomes; these are risks and opportunities (essentially positive risk). In these newer standards, assessing top-level strategic risks and opportunities is function of the planning clause; clause half-dozen.
- Comeback – Whatsoever improvement activities that you accept to make the processes of your management system better are preventive actions. The focus of the new requirements is for each company to discover good ways that piece of work for them to improve processes, rather than having the complicated preventive action arrangement in identify from previous versions of the standards. If you lot have something as uncomplicated as a suggestion program that identifies how to make processes better and implements those changes, this could exist an action to forestall a problem.
Information technology should exist noted that some other standards based on the ISO 9001 standard, including ISO 13485 and IATF 16949, however require preventive deportment. In both of these standards, the preventive action process is nonetheless intended to be the systematic process to address identified potential issues, rather than the comeback activities mentioned in a higher place.
Yous can acquire more than about how risk-based thinking is replacing preventive activity in the ISO 9001:2015 standard in this article: Risk-based thinking replacing preventive action in ISO 9001:2015 – The benefits
You can also read more on how Annex SL works in the commodity: Is ISO 45001:2018 compliant with Annex SL?
How do yous do corrective and preventive activity?
The systematic process for CAPA has not really changed in the newer ISO management organization standards, which are aligned with the ISO Annex SL format. Corrective actions are about improving behavior or performance of the process, and this hasn't changed. In general, you need to:
1) Identify the process problem – Ascertain what the problem really is. First, brand certain the trouble is, in fact, a real problem, and non a perceived trouble. A adept test is if you can write the problem with a requirement to compare, what is ofttimes chosen a "Should Be" and "Is" statement (e.m. Parts should be nickel plated, parts were received painted black). If you can't say what the outcome should be (or is expected to be), then y'all may non accept identified a real problem.
2) Identify how big the problem is – What is the scope of the problem? Make sure you lot empathize how large the trouble to be addressed is. Is it just today's production, or was yesterday's product affected too? Is it just this 1 production, or is it on more than than one production? Make sure you know what the trouble is, and more than importantly, what it is not. If the problem just happens on Wed, this may be important information.
3) Take action to contain the trouble – How can we stop the trouble while nosotros gear up the root cause? Make a correction to cease the trouble for correct now while you look for the ultimate cause and fix that. Basically, what firsthand checks or stop gap measures are you putting in place to make sure that yous will definitely take hold of the trouble again if it recurs while yous are fixing it.
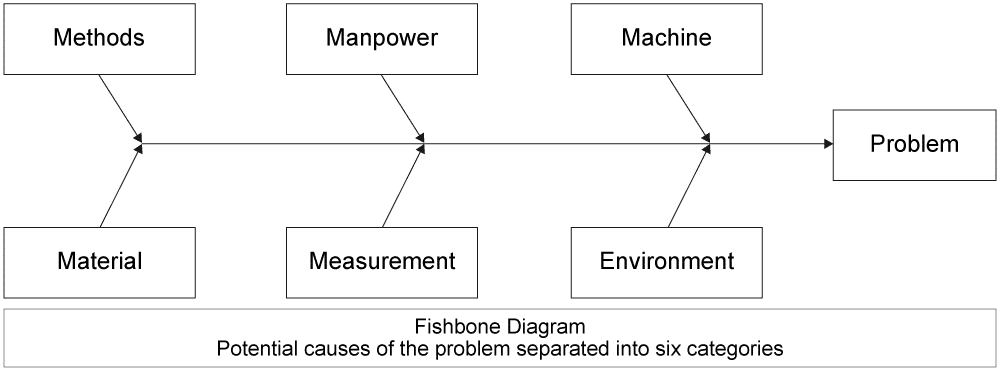
four) Place the root cause of the trouble – What is the base of the trouble, non just the surface manifestation? This is the trickiest part. How do you lot brand sure y'all have plant the underlying consequence? There are many different ways to practice this, from asking "Why" five times until you notice the ultimate crusade, to more than difficult methods like a classic Ishikawa (or Fishbone) Diagram. Whole grooming courses have been dedicated to this topic, only suffice it to say that y'all want to try to place the underlying problem, not just a surface trouble. After this step, it is wise to make sure that your telescopic has not become bigger, making further containment actions necessary.
5) Come with a programme to fix the root cause – What exercise you demand to alter to eliminate the root cause? Decide what steps are needed to eliminate the root crusade of the problem. Here, depending on the problem, yous will demand to identify the cost and return on investment. How will it exist funded (if information technology is a complicated and expensive fix), and who needs to approve the expense? Make certain the planned changes will non cause farther bug.
half dozen) Put your plan in place – Exercise what you have planned. This is every bit simple every bit following through on your plan and making it happen. It could exist as simple as implementing the preventive maintenance program already described, or buying and installing a new piece of equipment because the onetime 1 could no longer go along the accuracy you need.
seven) Check that your programme worked – Make sure your program was effective. Simply put, after you have fabricated your updates, wait a suitable amount of time and make sure the problem doesn't recur. If it does, you need to question if you got the actual root cause. This is the virtually important step, but too the step that most companies take trouble with. Often, people want to close out the paperwork chop-chop, or think the registrar requires closure early to demonstrate timeliness, just proper follow-up is essential.
Many companies volition take a cosmetic action class that follows this process, or a modified process, to capture the data and ensure that you do not forget whatever steps. Having a proficient systematic process is of import to find and gear up the root of the trouble for large, systemic issues within your system. If you lot only treat the symptom, so the problem will come back. The goal of corrective deportment is to correct the root of the problem, so the failure does non recur.
What is a cosmetic action plan?
The cosmetic activity plan is a prepare of actions to eliminate the problem. The cosmetic action plan is about addressing the root crusade of the problem, not simply correcting the symptom that has been found.
Any time yous have whatsoever nonconformity, you lot will exist taking steps to correct the nonconformity, but what you right is the difference between a unproblematic correction and a cosmetic activity. With a correction, you will address the most obvious problem so that you can remove the nonconformity and make the procedure acceptable to continue. This is a correction, which may be part of the containment actions.
Conversely, if you await at a trouble that has resulted in a nonconformity, and investigate the causes of that problem until yous understand the cause – which was the outset of the chain that resulted in the nonconformity (known as the root cause) – and you take deportment to correct this root cause then that it cannot happen again, you lot take taken a corrective action for the problem.
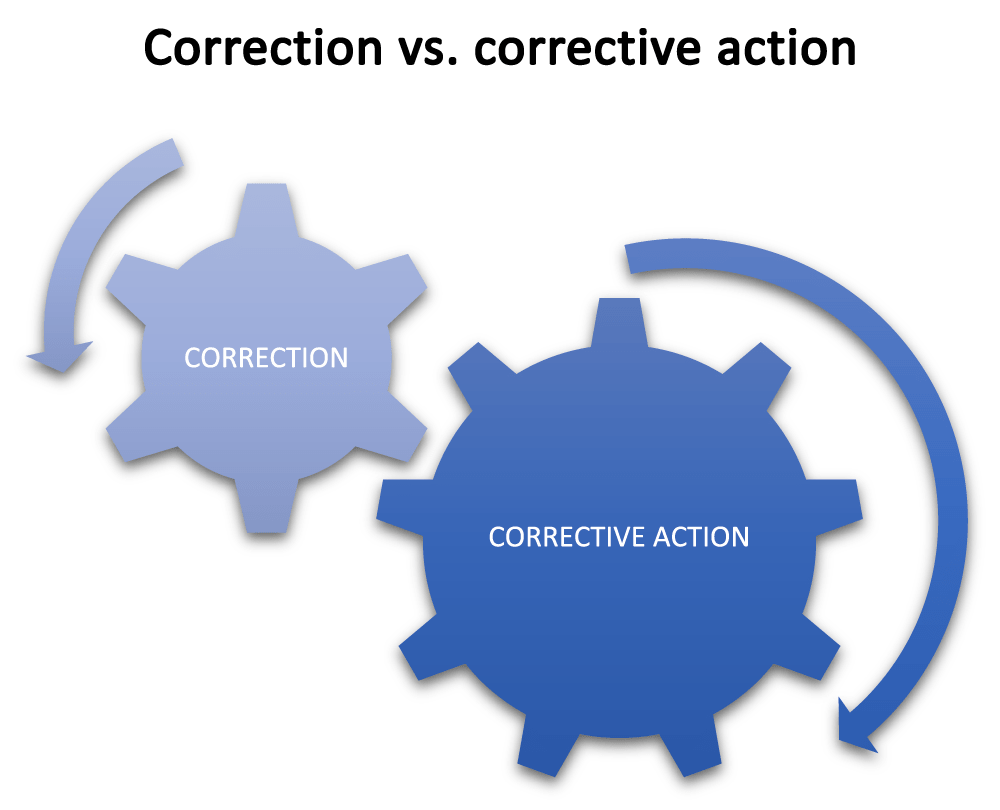
For example, adding in additional inspection may contain the process problem in the short term, only the corrective deportment will stop the trouble from occurring over again.
What should a corrective activity programme include?
When you accept identified the root cause of the problem, it is time to create a corrective action plan to eliminate it. Some things to call up about when preparing your corrective action plan include:
- Fully assessing the root cause – Have we fully assessed the root crusade, or could at that place be a further underlying cause to what has been identified?
- Assess the risks and opportunities of the change – It has e'er been important to make certain that the changes you lot have decided to brand are non going to cause more problems, but with the new version of the ISO standards there is a requirement to address the risks and opportunities that are present when you are going to make a change. For case, by making a process modify to address a root cause, is at that place a take chances that the output of the process will crusade a problem further on in your business organization, or fifty-fifty at your customer's site? If you have identified a proficient corrective action for one process, is there an opportunity that this can exist put in place for other processes to forestall problems from occurring in the future?
- Identify the steps needed – What are the steps needed to eliminate the root crusade from the procedure?
- Assess schedule & toll – What is the timeline of implementation? What are the toll and return on investment? Are there other alternatives that demand to be assessed? Is this programme viable?
- Program for assessment along the way – Every bit you work through your plan, practice y'all need to make changes? Assessing if the program is working as y'all continue tin can help to ensure that your final assessment for effectiveness volition requite authentic results.
- Plan for assessment of effectiveness – Before starting on the plan, how will we know the changes actually worked? Volition a primal functioning indicator ameliorate? Will we have to wait for several months to ensure the problem doesn't come up back (which would mean nosotros didn't address the root cause)?
As you can see, the corrective action plan is substantially equivalent to any other project programme y'all would create in your organization. It is important to ready expectations for how long the plan volition have, what resources volition be required, and when you will be completely done with the corrective activeness. It is an of import note that the ISO standards include a statement that the corrective deportment taken should be advisable to the significance of the effects presented by the nonconformities; so, information technology is not expected that you will spend an exceptional amount of time and money to address a small-scale problem. Retrieve this when you appraise the feasibility of the plan.
What is a preventive action program?
A preventive activeness plan, created for preventive actions, needs to include all of the same things that a corrective activeness programme does, as outlined in a higher place. If you are taking activeness to remove an identified risk, this should also exist treated like a project, with the same adequate oversight and budgeting of resources.
It is, of grade, of import to note that even a CA plan includes elements to prevent the trouble from happening in the future. The distinction of the PA plan is that information technology is implemented proactively for a potential problem, rather than as a reaction to an existing problem.
Why is corrective activity important?
When dealing with a systemic problem, one that is non due to a one-fourth dimension mistake, merely rather is acquired considering of something in the system, you tin can lose a lot of time and money by ignoring it. This is why corrective activeness is important. If people are performing unnecessary activities to continually fix problems that occur, or need to be constantly vigilant to catch problems that happen all the time before they go further, so you can relieve a lot of resources by taking the necessary actions to stop the bug from happening once again. The CA process is function of the Quality Management Arrangement to save you time and coin.
It is important to note that one of the issues with the corrective activity process is that it is difficult to use for modest, non-systemic issues where a root cause is not able to be institute. For this reason, the new ISO 9001:2015 standard (and others related to information technology, such as ISO 14001:2015 and ISO 45001:2018) has added into the requirements a decision later on you take corrected the trouble.
Once you have fixed the problem that was found, you can determine the need to accept action to eliminate the root crusade of the nonconformity. If you determine this is not needed, such as for a 1-time issue that shows no signs of recurrence, you tin can stop the corrective activeness process without going farther. You will still want to follow upward to ensure the problem does not recur and, if it does prove to be systemic, modify your decision and have further actions.
Of course, it is important to remember that some other standards based on the ISO 9001 standard, including ISO 13485 and IATF 16949, have non made this alter to decide on the need to address root cause.
When should a leader take corrective activeness?
Corrective action is about doing more only fixing a small trouble; information technology is about addressing a systemic issue that needs elimination rather than a small mistake that needs correction. So, a leader should accept corrective activity when a systemic trouble has been constitute. Some ideas for things leaders should review to look for potential systemic bug include:
- Central performance indicators (KPI) – Are there routine bug indicated by the performance indicators you accept called? Do your KPIs prove you that your processes are working properly?
- Review of records – Do your records testify regular problems that should be investigated, such every bit a cyclic delay that e'er happens on a sure date in the month?
- Feedback from employees – If at that place are employee suggestions of issues they are continually resolving, do you need to investigate further?
- Results of audits – Audits are used to indicate out where processes aren't coming together planned requirements, and assessing these shortcomings could indicate out systemic issues. This includes internal audits and customer audits, as well as certification audits.
How practice you lot implement corrective activity?
Implementing corrective activity is as simple as following the plan you lot have identified. Perform each footstep you accept identified, ensure it is completed satisfactorily, and assess that changes take non introduced new risks that you need to further address. Again, thinking of your CA plan every bit a project plan can aid you lot to empathize how implementation should proceed.
For implementation of a circuitous plan, you may want to use a Gantt chart to organize all of the activities, who volition be doing them, and by when. This type of tool can also indicate which activities can occur in parallel, and which need to wait until other actions take taken place. Fifty-fifty if you cull another method to rails your implementation, information technology is important to ensure that deportment are identified with resources, timelines, and how complete they are.
How practice yous write a corrective action study?
Every bit with any other study in an organisation, the cosmetic activity report can take whatever form is adequate in your visitor. Larger companies, with many people in pinnacle direction, may want formalized reports for big corrective actions – as they would for whatever project. These reports may include executive summaries, detailed outcomes and expenses incurred, and evidence for effective closure. Others may simply include a completed CAPA form as the written report.
In that location are some requirements for records to be kept in the ISO management system standards, and this should be included as part of your report, at a minimum. The ISO management system standards based on Annex SL, such as ISO 27001:2013, ISO 22301:2019, ISO 9001:2015, or ISO 14001:2015, require that the following be kept as CA records:
- The nature of nonconformities you have taken corrective actions for
- The actions taken in the corrective actions
- The results of the corrective actions, which would include the effectiveness
Remember that the process is at that place to help you to save resource by removing larger systemic bug from your organisation, rather than beingness a brunt to your company. Make certain you implement a CAPA system that volition work for you; not one that is just there for testify. Removing problems can exist one of the best means to make your organization better.
To acquire more than about how to use corrective actions for an internal audit, download this gratis white paper: How to perform an internal audit using ISO 19011
Source: https://advisera.com/blog/2021/07/19/complete-guide-to-corrective-action-vs-preventive-action/
0 Response to "Remove Action and Adding the Action Again"
Publicar un comentario